In 2005, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) adopted a new objective— To evaluate & measure the operational energy conservation of its Virginia Square facility and identify opportunities to further conserve energy and reduce utility costs.

OVERVIEW
The campus at the heart of George Mason University consists of an office building with office space and training facilities for FDIC employees, which houses the IT Data Center and an SRC for students and instructors attending classes. To complete this evaluation, FDIC used the services of KPMG, LLP.
KPMG identified several key drivers to improve the energy efficiency of the Virginia Square facility, including:
-
Reduce consumption
-
Reduce building operational costs
-
Measure and communicate stewardship
-
Reduce greenhouse gas emissions
-
Increase sustainability

KPMG was then charged with developing a formal Sustainability Program. The program development included engagement and support from the senior-most levels of the FDIC and providing sufficient personnel to manage the programs. The program’s main objective was to integrate divisional energy management and sustainability efforts with energy, water, waste, and emission management plans linked to future “Green” initiatives.
The program sets forth considerations for developing new policies and procedures for selecting green initiatives for consideration and for implementing the sustainability program:
CONSIDERATION #1 –
Program baselines, key performance indicators, evaluation approaches for measuring progress
CONSIDERATION #2 –
Adopting electricity, gas, and water sub-metering
CONSIDERATION #3 –
Installing an energy management system (Operations, Maintenance, and Measurement of Benefits)
CONSIDERATION #4 –
Increasing employee awareness by establishing internal and external communications of current green practices and strategies
CONSIDERATION #5 –
Adoption of a system for connecting collected rain water and storm water to a gray water system
CONSIDERATION #6 –
Adopting WaterSense cost reduction techniques (purchasing non-potable vs. potable water)

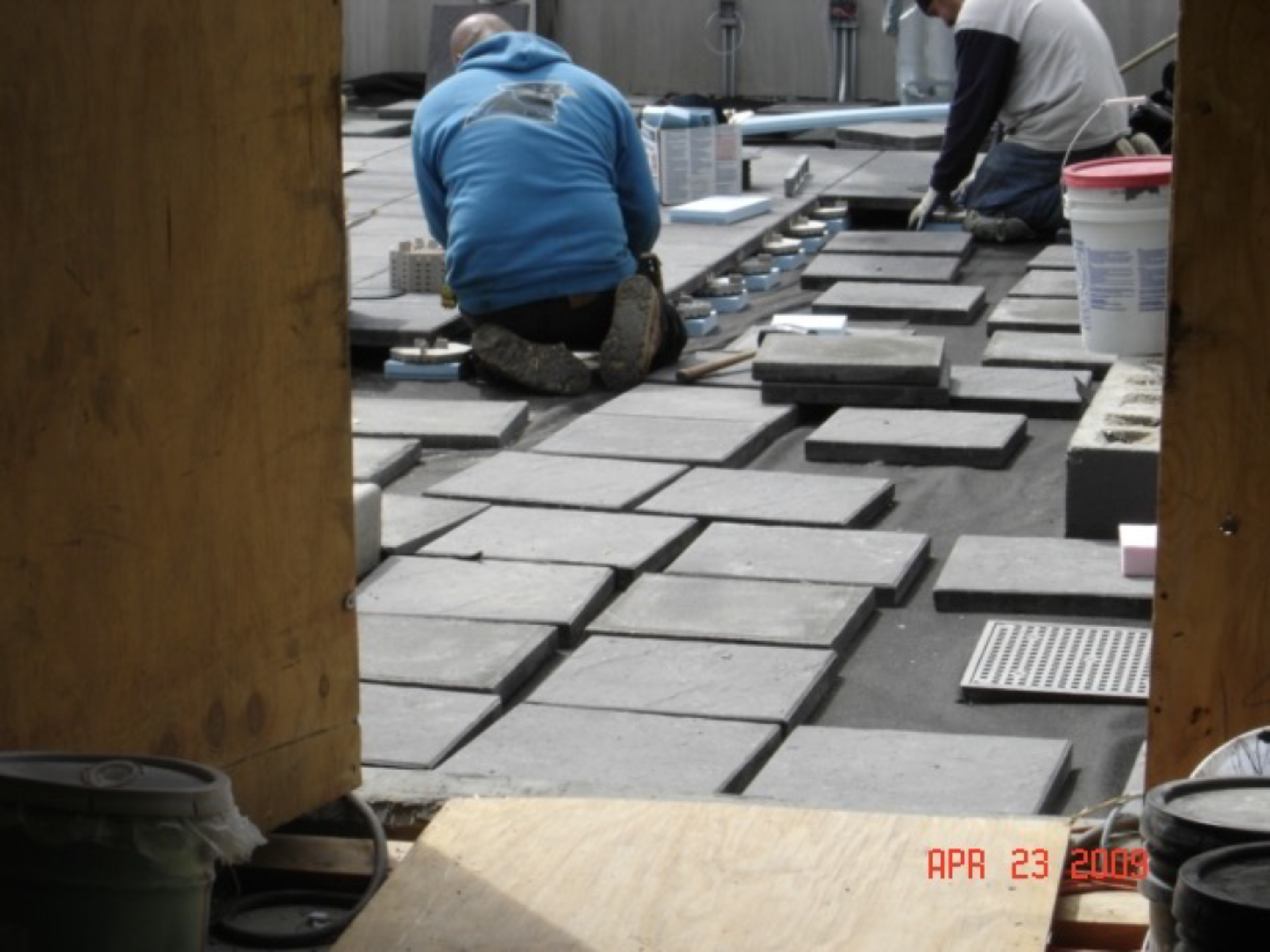
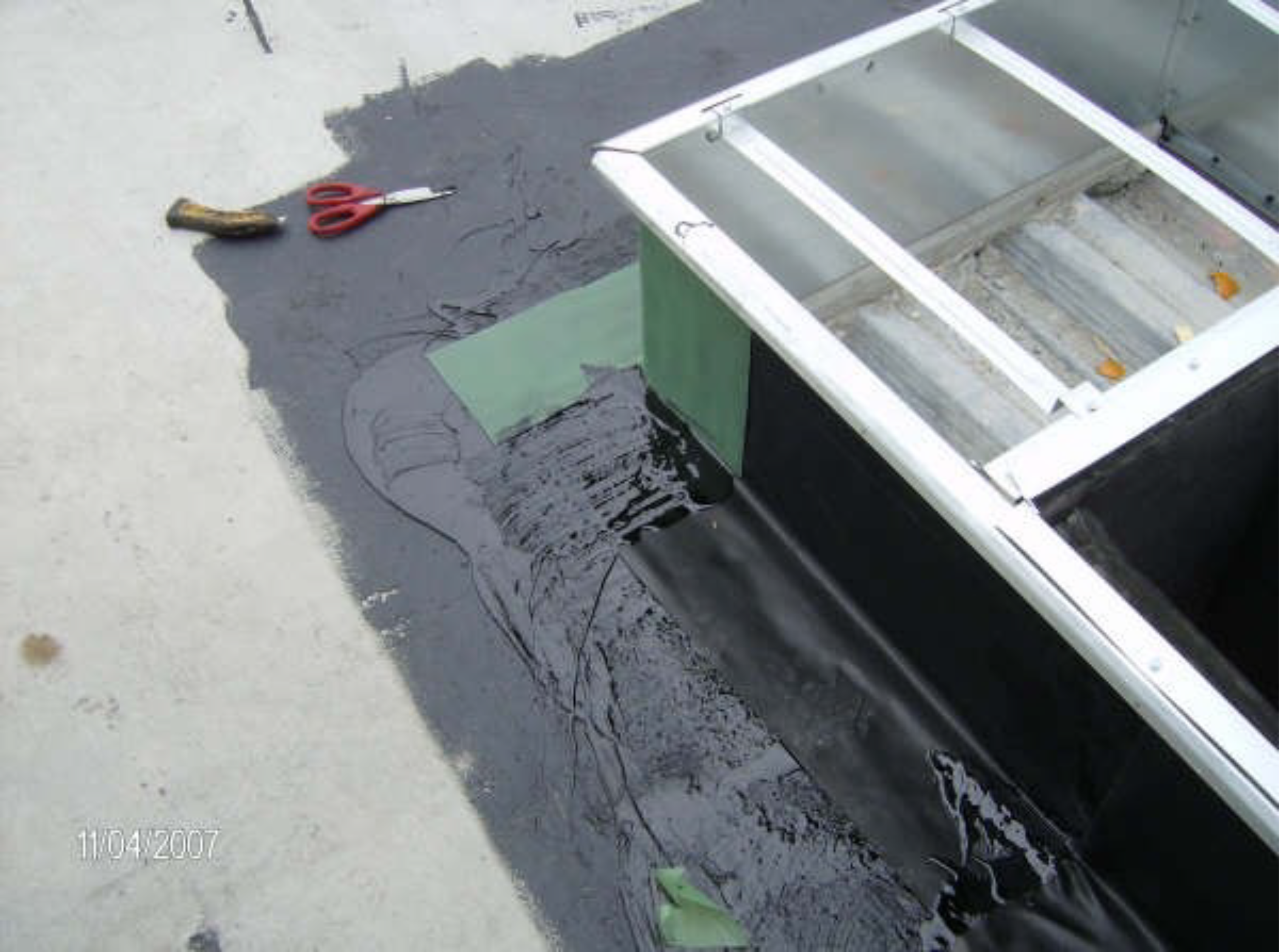
PICTURED: Preparation of the deck on the rooftop of the FDIC Building, including clearing away all debris, before it is ready to receive a prime coat.
A SOMEWHAT “GREEN” CONCEPT…
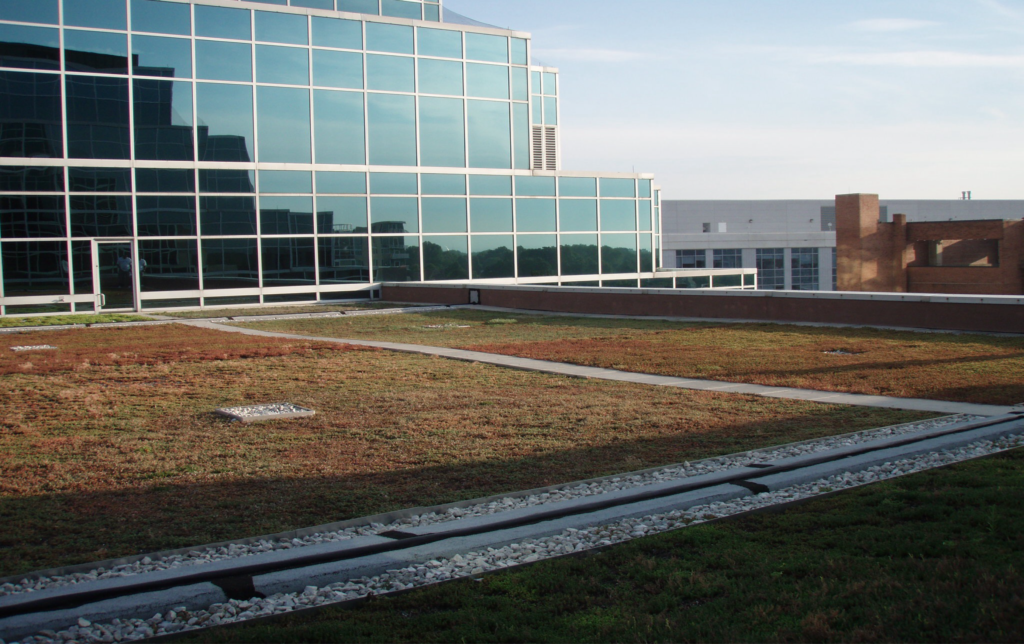
One of the primary efforts for improving energy management & sustainability was the addition of an extensive green roof, an idea that was far less common than it has become in recent years.
Presiding over the 7th floor of the building annex, the 2,900 square foot green roof atop the FDIC Virginia Square campus is one of the first completed federal green roofs in the Washington D.C. metro area, having been completed on July 15, 2005. Installed over the single-source Barrett Greenroof-Roofscape® system, it was designed to maximize storm water retention, thereby protecting area rivers from stormwater runoff.

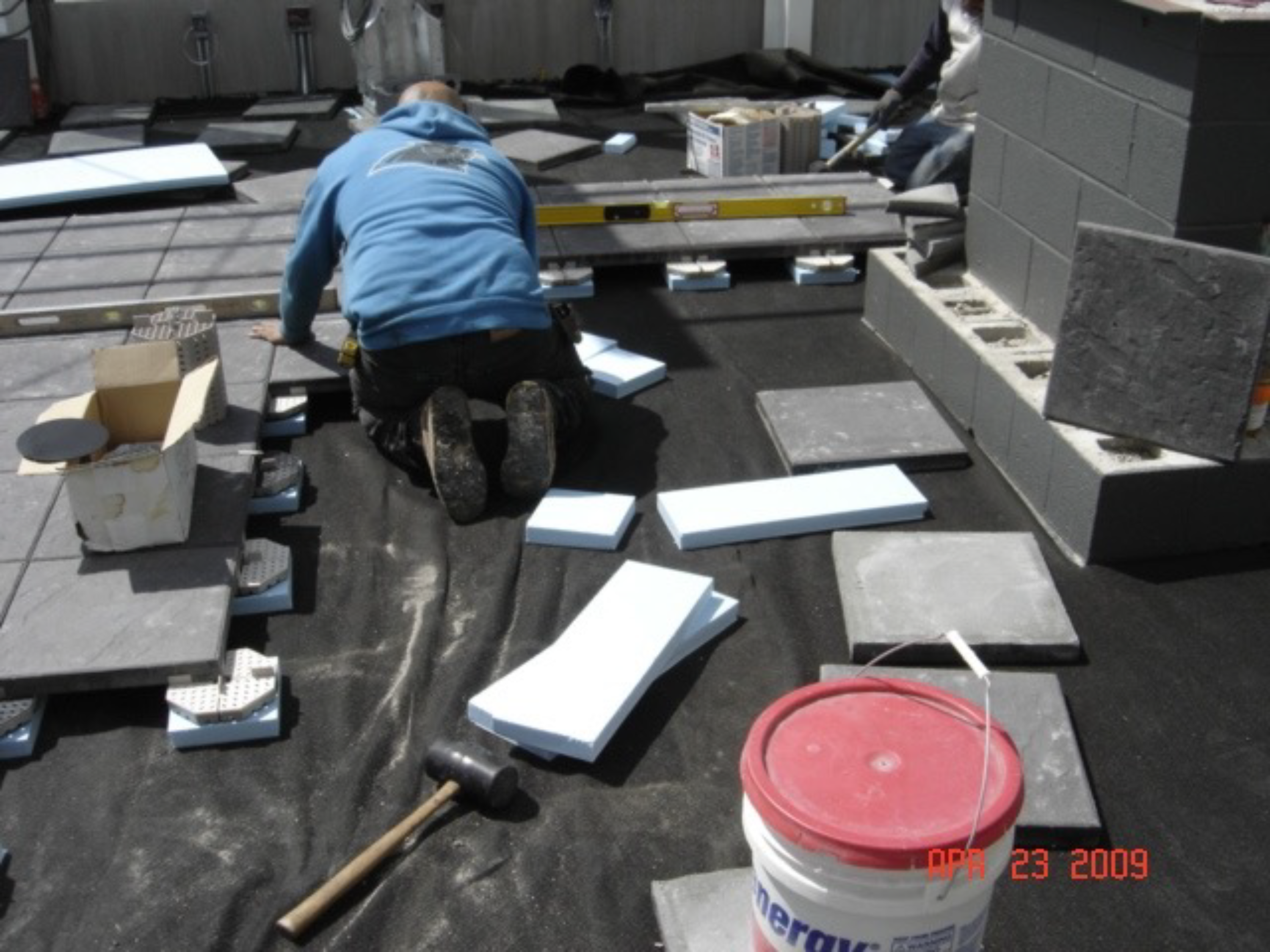
PICTURED: Installation of Roofscape® metal edging & termination materials.
THE SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The FDIC building’s green roof utilizes a PMR/IRMA® assembly. The waterproofing system consists of 215 mils of Barrett’s RamTough 250 hot fluid applied rubberized asphalt with a PolyFelt 125VP polyester reinforcement fabric and a Ram 203 SBS-modified protection course. Above that, there is a layer of RB 20 root barrier, XPS insulation, and a drainage/retention mat.
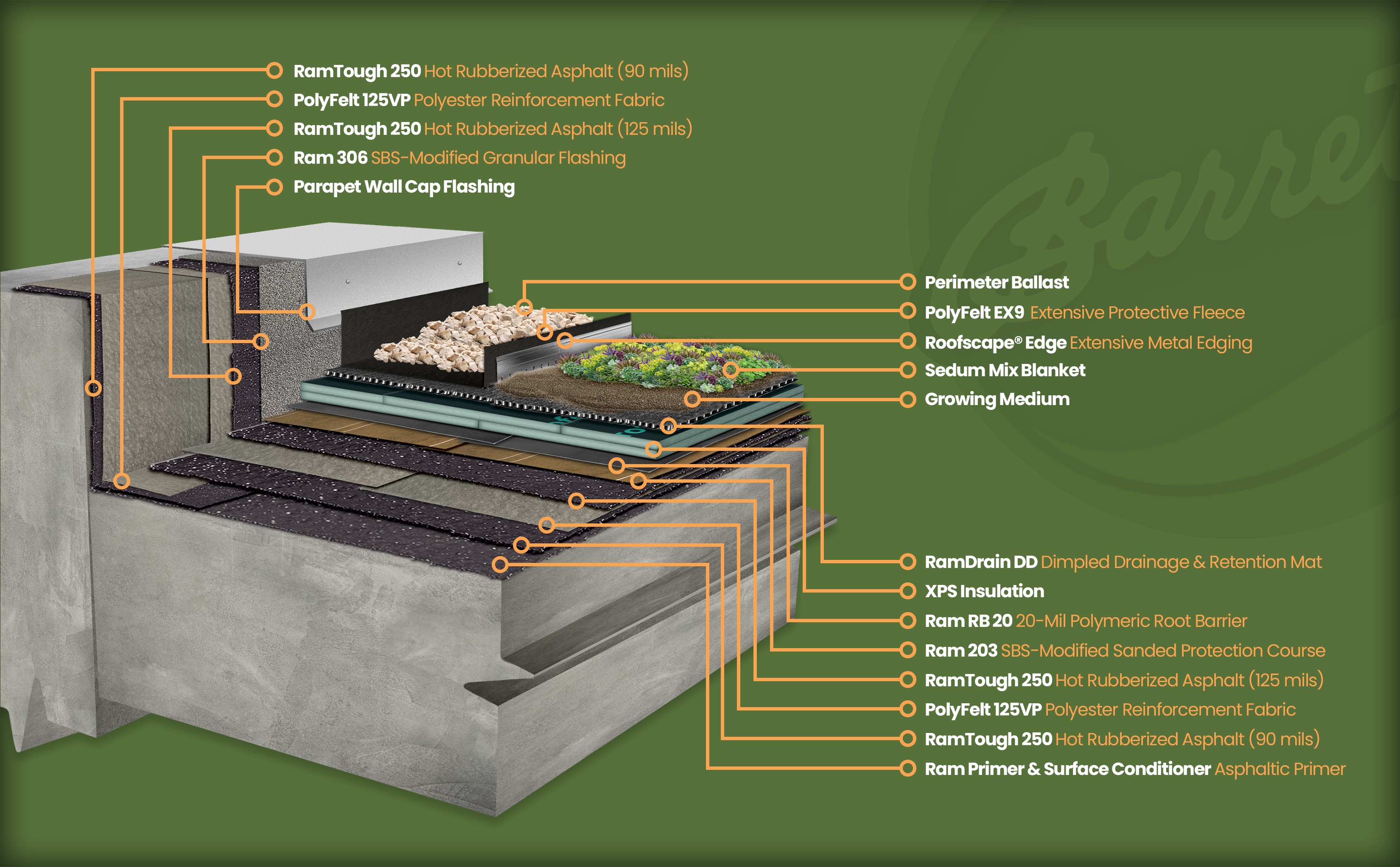
PICTURED: System components of the FDIC Virginia Square Extensive Greenroof-Roofscape® assembly.
THE CHALLENGE
There are over 12,000 sedums planted at 6 inches on center for rapid coverage. The project took 15 days, and due to extremely challenging construction logistics, required hoisting the soil, gravel and other materials onto the 8th floor roof of the South Tower, then lowering it to the 6th floor roof of the building annex, then up again to the 7th floor annex roof for installation.

PICTURED: Rock ballast being poured around perimeter. Due to extremely challenging construction logistics, the soil, gravel and other materials had to be hoisted onto the 8th floor roof of the South Tower, then lowered to the 6th floor roof of the building annex, then up again to the 7th floor annex roof for installation.
THE RESULTS?
Visually, the green roof is an aesthetic plus for the employees as it can be viewed by anyone from the glass façade of the South Tower. More importantly, the performance data collected from the green roof will outweigh its beauty tenfold.
This green roof allowed the developers to offset very high onsite storm water management fees assessed by the county. The installation over Barrett’s contributes to the program with recycled water at 50% non-potable use, collecting rainwater and storm water and directing it to the gray water system. This one consideration added valuable LEED credit 5.1 @ 25% usage with additional credit 5.2 @ 50% usage.
Arlington Cable Access filmed a documentary on green roofs and D.C. Greenworks during the installation of this roof. It was aired on Arlington Cable Access in the fall 2005.

PICTURED: Vegetation growth on the FDIC Virginia Square rooftop after two years.
Want to learn more about our Greenroof-Roofscapes®?
CLICK HERE